What is an exchange rate between currencies?
If you have ever exchanged one currency for another while traveling abroad, you will know that currency exchanges are denoted in pairs. For example, EUR/USD, GBP/USD, CHF/JPY, are all examples of currency pairs.
An exchange rate is the value of one currency expressed in terms of another and determines how much of one currency is needed to buy a unit of another and is a fundamental concept in international trade and finance.
There are two types of exchange rates - Floating and fixed. A floating exchange rate is determined by supply and demand in the forex market and can change rapidly. This is one of the fundamental factors affecting the currency exchange rate, as every volatile pair consists of two floating currencies.
On the other hand, a fixed exchange rate is set by a country’s central bank and remains constant and stable relative to another currency. For example, the Saudi riyal (SAR) is pegged to the U.S. dollar at a stable rate of 3.75.
Major factors affecting the exchange rate
Now that we have established the meaning of an exchange rate, we can look at some of the most influential factors affecting exchange rates between currencies and whether it is possible to effectively hedge against them to avoid losses.
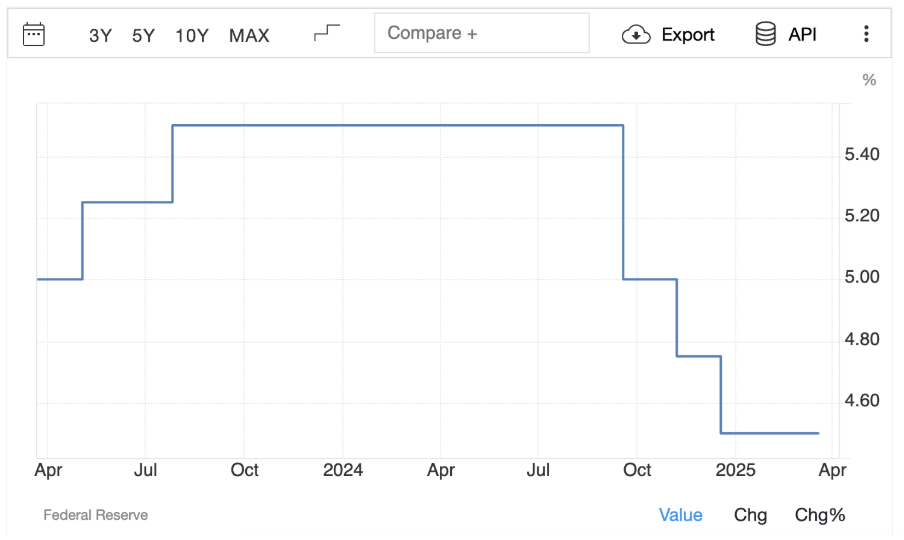
Interest rates
Perhaps the most determining factors in exchange rate fluctuations, interest rates are set by a country’s central bank and seek to ensure price stability within the economy.
Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, primarily to the bond market, which increases the demand for local currency, strengthening its value.
Conversely, lower interest rates have the opposite effect and lead to a weaker currency.
For example, if the Federal Reserve of the United States raises interest rates, while the European Central Bank does not, the exchange rate will shift in favor of the USD, due to a strengthening dollar, as investors sell the euro against the dollar due to higher treasury notes and bond yields in USD.
Inflation
Another one of the top determinants of currency pair values is inflation, which erodes the purchasing power of a currency. Countries with low and stable inflation tend to have stronger currencies, as their money retains value over time. In contrast, high inflation devalues a currency, leading to depreciation.
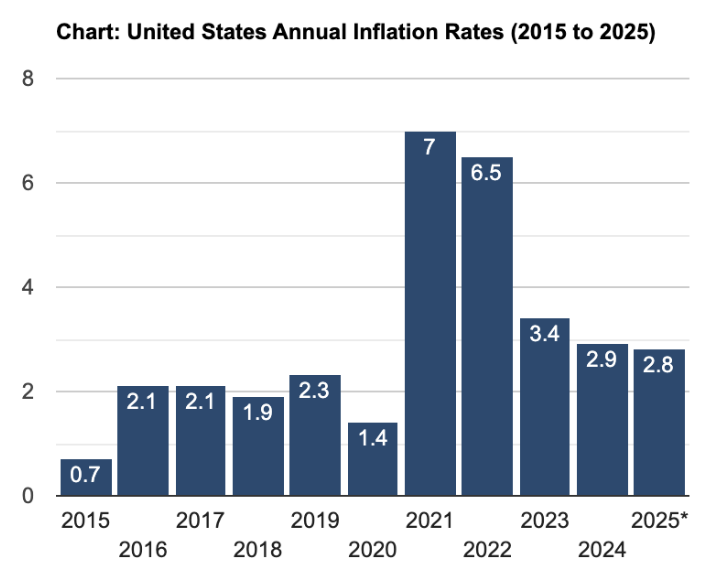
For instance, if the UK experiences higher inflation than the United States, the British pound (GBP) is likely to weaken against the U.S. dollar, as goods and services in the UK will become more expensive, reducing foreign demand for the currency. Inflation greatly affects central bank policy, which means that the Bank of England would promptly raise rates to combat inflation.
Economic growth
A country’s overall economic health is often measured in GDP. While a notoriously unreliable indicator, countries with strong economic growth tend to have stronger currencies with stable and low inflation and a lot of foreign investment.
One of the notable factors affecting the exchange rates between currencies, economic growth is an important metric for numerous reasons. Investor confidence is a good example, as resilient economic growth leads to more optimism towards the future prospects of the economy, which paves the way for long-term investments - further strengthening the local currency.
Exchange rate appreciation is a common byproduct of economic growth, as the local market, coupled with international investors, maintain a bullish stance for the future, boosting currency demand.
Political stability
One of the most important factors affecting exchange rates between two currencies is political stability. For example, if two countries are at peace and the economies are growing steadily, the performance of their respective currencies is also likely to be relatively stable.
On the other hand, if one country is embroiled in conflict, this destabilizes the financial markets as well, reducing the demand for their currency and tanking the exchange rate with other countries.
Therefore, peace and stability are integral parts of exchange rates and once stability has been compromised, the exchange rates quickly follow.
It is also worth noting that the destabilizing effects need not be as severe as a military conflict or civil war. General social unrest, mass protests and demonstrations, can also erode the confidence of investors and the local consumer base in the prospects of the country. For this reason, good governance is one of the critical factors impacting currency pair exchange rates
Balance of trade
A country’s balance of trade, which is the difference between exports and imports, influences exchange rates to a considerable extent.
In fact, it is considered to be one of the most important factors influencing currency exchange rates in forex and is closely monitored by analysts and investors alike.
If a country exports more than it imports, demand for its currency increases, leading to appreciation. Conversely, a trade deficit weakens a currency due to more local currency being sold to purchase foreign goods.
The current account balance, which includes trade balance and foreign investments, also impacts exchange rates.
For example, the United States typically runs a deficit, but makes up for it through foreign investments and demand for U.S. assets.
Market speculation and investor sentiment
In the context of the forex market, one of the most important factors affecting exchange rates between two currencies is market speculation.
Every day, millions of forex traders enter the market and trade currencies alongside major financial institutions, which can have a noticeable effect on the exchange rates of two currencies. When traders sense opportunities on the market, they either go long or short on a particular pair, which is further exacerbated by the use of leverage, which can be as high as 1:500 or 1:1000, depending on the brokerage firm. Therefore, trader sentiment is a notable factor in the fluctuations on the currency market.