The most important indicators in Forex
In Forex, as well as other trading markets, there are lots of different elements that influence trading outcomes. Traders can use different kinds of charts for technical analysis, automate their trades with trading bots (
Expert Advisors, cBots, etc.), or use technical indicators to make better predictions about the future price movements.
When it comes to Forex indicators, there is a huge selection of them, both pre-existing and custom made. Many pieces of software, including MetaTrader or cTrader, allow traders to create their own technical indicators and incorporate them into the platform. Therefore, there is no shortage of these indicators at all.
As for the most important indicators, it all comes down to what traders choose for their specific trades. However, there are still some indicators that are widely known and used across the platform. These are:
- Moving Average (Simple and Exponential)
- Moving Average Convergence/Divergence (MACD)
- Bollinger Band
- Fibonacci Retracement
We will discuss these technical indicators in this article.
The Moving Average
First off, let’s start with probably the most basic technical indicator, the Moving Average. This indicator uses the historical price movements of an asset and offers traders their average (mean).
The Moving Average itself can be divided into two different indicators: a Simple Moving Average (SMA) and an Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The SMA and EMA can be considered the top Forex indicators because in many cases, they also help create other indicators.

A Simple Moving Average
The SMA is just an average of all the prices that occurred in a given period of time. For example, if we want to get a Simple Moving Average for 20 days, we have to get a sum of every price in this set and then divide them by 20, which gives us the mean of the closing prices during those 20 days.
The SMA is a so-called “lagging” indicator because it offers the trend for the historical prices after the trend has already begun. What’s more, the SMA isn’t the best indicator in Forex for identifying the influence a sudden price change has on the overall trend. The reason for that is that as time goes on and the number of individual prices increases, the average number becomes less sensitive - an additional price doesn’t affect this number that much.
But this doesn’t mean that the SMA has no use. It is a very useful indicator for actually confirming a trend. Usually, the Simple Moving Average operates with two data sets (sometimes more): one for a shorter time period and one for a longer time period.
When the long-term average crosses the short-term average, the SMA indicates the beginning of a new trend. We have an uptrend if the long-term line is moving above the short-term line, and we have a downtrend if the long-term line is moving below the short-term line.
An Exponential Moving Average
The EMA is quite similar to the SMA in that it also offers the average of the historical prices. However, at the same time, this indicator focuses more on recent prices and is more sensitive to the current price changes. That’s why in this list of Forex indicators, the EMA is more widely used for making sophisticated predictions.
Typically, short-term averages use 12-day and 26-day data sets, whereas long-term averages have 50-day and 200-day data sets. Similar to the SMA, the trading signals occur when the lines cross each other. If the shorter moving average (MA) crosses the slower MA and goes above, the signal suggests buying an asset. And if the shorter MA crosses below the slower MA, the signal will suggest selling an asset.
The Moving Average Convergence/Divergence (MACD)
This next technical indicator, as its name suggests, also uses the average levels to identify a trend. But it doesn’t just stop at that: the MACD goes as far as giving the strength/momentum of that trend. It does that by calculating the difference between the faster and slower EMAs.
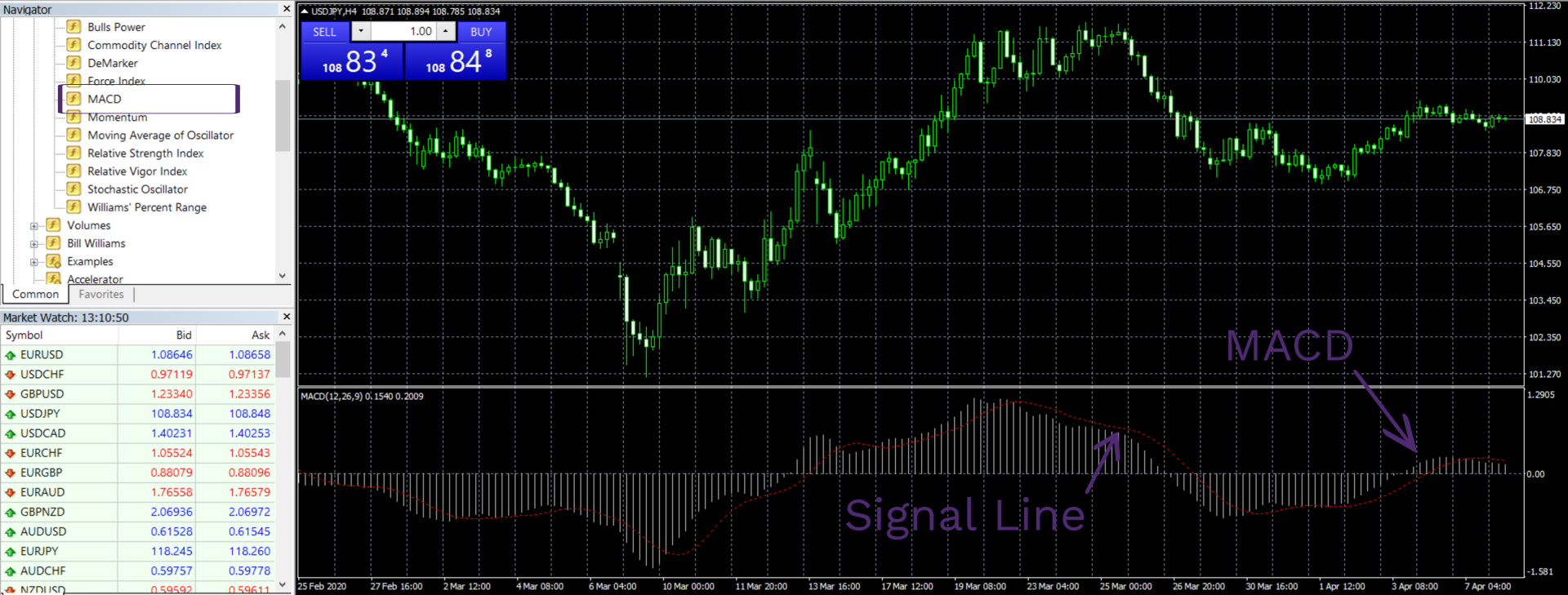
Basically, the MACD line can be calculated by subtracting the 26-day EMA from the 12-day EMA, which gives us the strength of the trend. Then, a 9-day EMA is put in the chart as a signaling line. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, the indicator gives out a buying signal, whereas the crossing below the signal line will give out the selling signal.
The Bollinger Band
The previous indicators mainly focused on providing the average level of the previous prices. As for which Forex indicators to use for calculating the volatility of an asset, the
Bollinger Band is probably the best Forex indicator choice.
The Bollinger Band is a volatility channel that signals the amount of change an asset took from the average point. In short, this indicator uses standard deviations to offer the volatility of a currency pair or another asset.

Visually, the Bollinger Band consists of three lines - one moving average and two standard deviation lines. The two deviation lines indicate how far the asset prices diverge from the average price. This way, traders get more specific data about the shifts in prices.
Fibonacci Retracement
Finally, let’s talk about Fibonacci Retracement and how to use Forex indicators like that in actual trades. First off, we have to note that Fibonacci Retracement is based on the famous Fibonacci sequence that has been known to humanity from ancient times, but was officially systematized by the Italian mathematician, Fibonacci. The sequence begins with 0 and 1 and the next numbers are the sums of the previous two numbers. This is how this goes: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13…
The idea behind Fibonacci Retracement is the belief that when the market makes an extreme move - whether it’s a sudden increase or sudden decrease in price, - the chances are, it will soon go back to its prior position by the given ratios.
These ratios come from the numbers in the Fibonacci sequence. The key ratio is 0.618, or 61.8%. It can be calculated by dividing a number from the sequence by the next number immediately following it in the same sequence. As we move forward in the Fibonacci set, the ratio increasingly moves closer to 61.8%. For example, 34/55=0.61818 and 144/233=0.61802.

The next important ratio is 0.382, or 38.2%. We get this ratio by dividing a number by the one that is two places ahead of it in the sequence. For instance, 55/144 or 89/233. Again, we get closer to this ratio as we move forward in the sequence. There’s also a 0.236 ratio (23.6%) which is a ratio between a number to the one that’s three places ahead of it.
So, the idea behind all these numbers and ratios is that after a drastic price move, that same price will probably get back to where it was and the amount by which it will retract will coincide to the Fibonacci ratios. Using the Fibonacci Retracement, traders can make certain predictions as to how the price of a given asset will increase/decrease after a major price move.